Top Rolling Mill Machine Types for Industrial Applications?
The rolling mill machine plays a vital role in various industrial sectors. It shapes metals through compression, enabling efficient production processes. Different types of rolling mills cater to specific needs, enhancing versatility in manufacturing.
Industries utilize these machines for creating products like sheets, plates, and bars. Each rolling mill machine type offers distinct advantages. For instance, hot rolling mills are ideal for large-scale production, while cold rolling mills provide tight tolerances and better surface finishes.
However, selecting the right rolling mill machine can be challenging. Organizations must consider factors like material type and production volume. Continuous improvement and adaptation are crucial in this fast-evolving landscape. There’s always room for growth and insights in optimizing rolling mill operations.
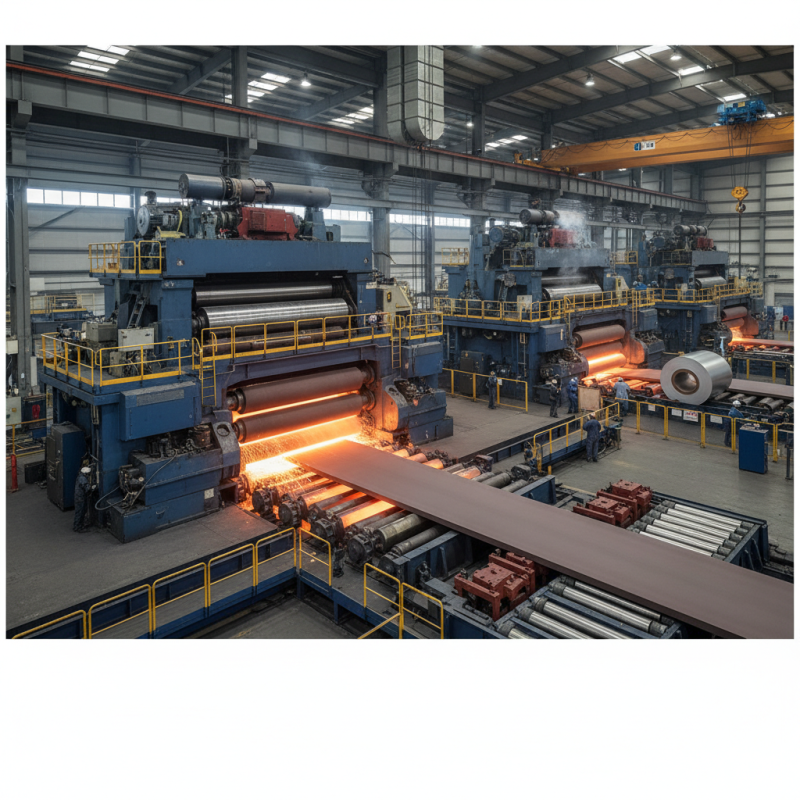

Types of Rolling Mill Machines Used in Modern Industries
Rolling mill machines play a crucial role in modern industries, especially in metal processing. Various types of rolling mills are employed to shape and size metals into the desired forms. These machines significantly impact production efficiency and product quality.
The most common types of rolling mills include two-high, three-high, four-high, and cluster mills. Two-high mills consist of two rolls and are ideal for simple tasks like hot rolling. According to a recent industry report, around 40% of the global rolling mill market is dominated by two-high designs. In contrast, four-high mills have a configuration that allows them to handle thicker materials efficiently. They are favored for their ability to control sheet thickness with high precision.
Cluster mills utilize multiple rolls and are suitable for thin materials. These machines can produce thin strips without compromising on thickness control. Industry data indicates a growing demand for cluster mills, particularly in the aluminum sector.
Understanding different types of rolling mills helps industries select the right machine. It directly affects productivity and product characteristics. However, making a choice can be challenging with numerous options available.
Key Features and Functions of Different Rolling Mill Types
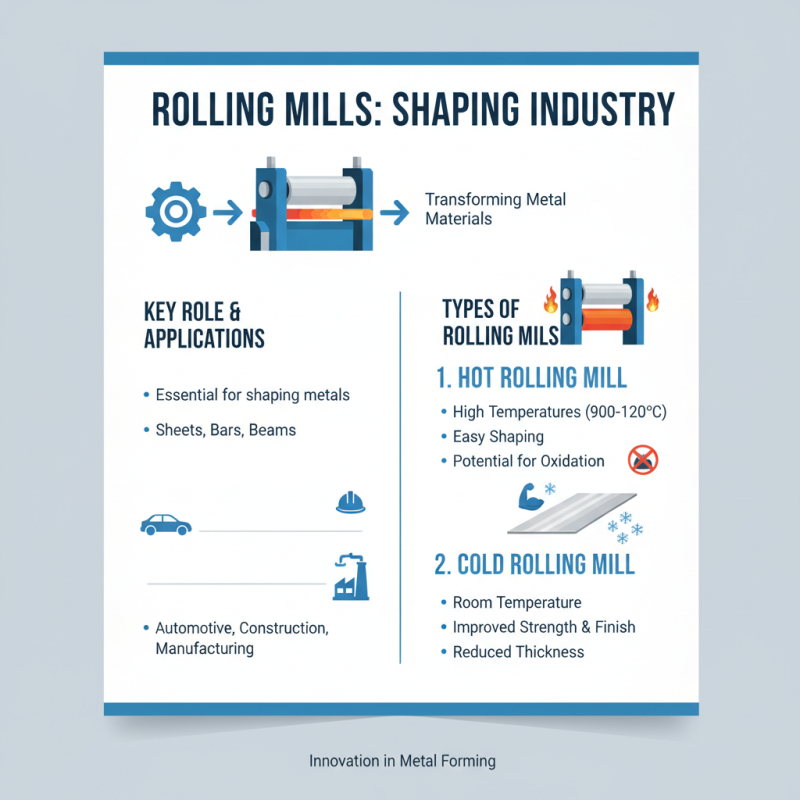
Rolling mills play a crucial role in various industrial applications. These machines are essential for shaping and transforming metal materials. There are several types of rolling mills, each designed for specific tasks. Hot rolling mills process metal at high temperatures. This method allows for the easy shaping of materials into sheets, bars, and other shapes. However, with heat comes oxidation, which might compromise the final product's quality.
Cold rolling mills, on the other hand, work at room temperature. They provide superior surface finishes and tighter tolerances. This method is ideal for producing metal strips and foils. But it can lead to greater material hardness. Understanding the different features of these mills is key. For example, tandem rolling mills consist of multiple stands. They enhance productivity but require precise settings to avoid defects.
Another type, the cross-country mill, efficiently rolls heavier materials. It can also easily handle diverse width requirements. However, its complexity poses challenges in operation and maintenance. The selection of the right rolling mill should consider both the product outcome and production efficiency. Finding a balance is essential for achieving desired results while minimizing issues.
Advantages of Hot Rolling vs. Cold Rolling Processes
The choice between hot rolling and cold rolling processes significantly impacts the properties of the final product. Hot rolling takes place at high temperatures, typically above the recrystallization temperature of the material. This process produces a finished product with superior ductility and strength. According to industry data, hot-rolled steel exhibits a yield strength that is approximately 25% higher than its cold-rolled counterpart.
Cold rolling, performed at room temperature, can enhance the surface finish and tolerance of the metal. However, it typically involves greater energy consumption, making it less efficient for high-volume production. The thickness reduction achieved through cold rolling allows for intricate shapes. Studies reveal that cold-rolled products can retain a tighter thickness tolerance, improving compatibility in subsequent manufacturing processes.
**Tip:** Consider the end use of the product when choosing between hot and cold rolling. If the application requires detailed precision, cold rolling might be ideal. For structural applications, hot rolling may be more suitable due to its mechanical properties.
While hot rolling is less expensive and more energy-efficient, it can lead to surface defects if not monitored properly. Conversely, while cold rolling may produce a high-quality finish, the higher production cost and longer processing times could be challenging for some manufacturers. Balancing these factors is crucial for optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Applications of Rolling Mills in Various Industrial Sectors
Rolling mills play a crucial role in various industrial sectors. They are essential in producing flat and long products. In the automotive industry, rolling mills help create lightweight components. These components improve fuel efficiency and enhance vehicle performance. Manufacturers rely on consistent quality from these machines.
In the construction sector, rolling mills are vital for producing beams and sheets. These materials are used in buildings and infrastructure. The process requires precision to ensure strength and durability. Not all mills deliver the expected outcome. Some may produce inconsistencies in thickness. This can lead to waste and increased costs.
The energy sector also benefits from rolling mills. They are used to manufacture parts for wind turbines and pipelines. The need for strong and reliable materials is critical here. However, not all mills meet the high standards required. It is a continuous challenge for industries to find the right equipment. Balancing quality and production efficiency remains a hurdle.
Top Rolling Mill Machine Types for Industrial Applications
| Type of Rolling Mill | Application | Material Processed | Industry Sector |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Rolling Mill | Producing sheets and plates | Steel, Aluminum | Construction, Automotive |
| Cold Rolling Mill | Finishing surfaces and dimensions | Copper, Stainless Steel | Electronics, Appliances |
| Cluster Rolling Mill | High precision thickness reduction | Titanium, Nickel Alloys | Aerospace, Defense |
| Plate Rolling Mill | Bending and forming plates | Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel | Shipbuilding, Manufacturing |
| Shape Rolling Mill | Producing structural shapes | Steel | Construction, Infrastructure |
Future Trends in Rolling Mill Technology and Innovations

The future of rolling mill technology is fascinating. Innovations are driving efficiency and productivity in industrial applications. Automation is at the forefront. Smart software systems are optimizing processes. These systems can predict maintenance needs and prevent downtime. Real-time data analysis enhances decision-making, leading to improved quality.
Tips: Invest in training for your staff. Understanding new technologies is crucial. Maintain clear communication channels in your team. This fosters collaboration in implementing new systems.
Another trend is eco-friendly operations. Energy-efficient machines minimize waste and energy consumption. Sustainable materials are gaining traction. Manufacturers are exploring alternative steel production methods. This focus on sustainability presents both a challenge and an opportunity. Adapting to these changes is essential. Transitioning to greener technologies can require significant investment and time.
Tips: Regularly assess your processes for waste reduction opportunities. Collaborate with partners who share your sustainability goals. Staying informed about industry trends helps maintain a competitive edge.
Related Posts
-

Top Tips for Choosing the Right Rolling Mill Machine?
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Best Cold Rolled Slitter Machine
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Best Roller Mill Machine for Your Needs
-

Why You Need a Roll Straightener Machine for Efficient Metal Processing
-

Top 10 Coil Shearing Machines for Precision and Efficiency in Metal Processing Industry
-

2026 Best Hot Rolling Mill Machine Insights and Innovations?
